UNIVERSAL QUANTIFICATION FOR SELF-ORGANIZED CRITICALITY IN ATMOSPHERIC FLOWS
A.Mary Selvam
Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune - 411 008, India
Proceedings(Poster) Conference on Patterns,Nonlinear Dynamics and Stochastic Behaviour in Spatially Extended Complex Systems,October 24-28,1997,Budapest,Hungary
Atmospheric flows exhibit selfsimilar
fluctuations on all scales (space-time) ranging from climate
(kilometers/years) to turbulence (millimeters/seconds) manifested
as the fractal geometry to the global cloud cover
pattern concomitant with inverse power law form for power spectra
of temporal fluctuations. Selfsimilar fluctuations implying
long-range correlations are ubiquitous to dynamical systems in
nature and are identified as signatures of self-organized
criticality. Standard models in meteorological theory
cannot explain satisfactorily the observed self-organized
criticality in atmospheric flows. Also, mathematical models for
simulation and prediction of atmospheric flows are nonlinear and
computer realizations give unrealistic solutions because of deterministic
chaos, a direct consequence of finite precision round-off
error doubling for each iteration of iterative computations
incorporated in long-term numerical integration schemes used for
model solutions (References). An
alternative non-deterministic cell dynamical system model [A.Mary
Selvam,Can.J.Phys.68(1990)831] predicts the observed
self-organized criticality as a direct consequence of quantumlike
mechanics governing flow dynamics.The model concepts show that
the centripetal acceleration representing the inertial mass of
eddy circulation follows inverse square law form analogous to
Newton's third law for planetary motion.
MODEL CONCEPTS
Atmospheric flows is a representative example
of turbulent fluid flows.The model is based on the concept that
spatial integration of enclosed small scale(turbulent eddy)
fluctuations result in organized large eddy circulations. The
eddy energy spectrum therefore follows statistical normal
distribution characteristics according to the Central Limit
Theorem. Therefore,the square of the eddy amplitude,i.e.,
variance represents the statistical normal probability density
distribution.Such a result that the additive amplitudes of
eddies,when squared, represent probability densities is observed
in the sub-atomic dynamics of quantum systems such as the
electron or photon. Atmospheric flows therefore follow
quantumlike mechanical laws. The root mean square(r.m.s)
circulation speed W of large eddy of radius R
is then given in terms of enclosed small scale eddy circulation
speed w and radius r as
W2=(2/p)(r/R)w2..........................(1)
The square of the eddy amplitude W2 represents the kinetic energy E given as(from Eq.1)
E=HnR........(2)
where nR
( proportional to 1/R ) is the frequency of the
large eddy and H is a constant equal to (2/p)rw2
for growth of large eddies sustained by constant energy input
proportional to w2 from
fixed primary small scale eddy fluctuations. Energy content of
eddies is therefore similar to quantum systems which can possess
only discrete quanta or packets of energy content hn ( where h is
a universal constant of nature ( Planck's constant)
and n is
the frequency in cycles per second of the electromagnetic
radiation.
The relative phase angle between large and
turbulent eddies is equal to r/R and is directly
proportional to W2 (Eq.1).
The phase angle therefore represents variance and also there is
progressive increase in phase with increase in wavelength. The
above relationship between phase angle,variance and frequency has
been identified as Berry's Phase in the subatomic
dynamics of quantum systems.Writing Eq(1) in terms of the
periodicities T{=2(p)R/W}
and t{=2(p)r/w}
of large and small eddies respectively we obtain
R3/T2=(2/p)(r3/t2)......................(3)
Equation(3) is analogous to Kepler's
third law of planetary motion,namely, the square of the
planet's year(period) to the cube of the mean distance from the Sun
is the same for all planets and results in inverse square law
analogous to the Newton's inverse square law for
gravitation. The model is similar to a superstring model
for subatomic dynamics [M.Kaku, New Scientist 18 Jan, 1997, 32]
which unifies quantum mechanical and classical concepts and
incorporates gravitational forces along with nuclear and
electromagnetic forces.The cumulative sum of centripetal forces
in a hierarchy of vortex circulations may result in the observed
inverse square law form for gravitational attraction between
inertial masses(of the eddies).
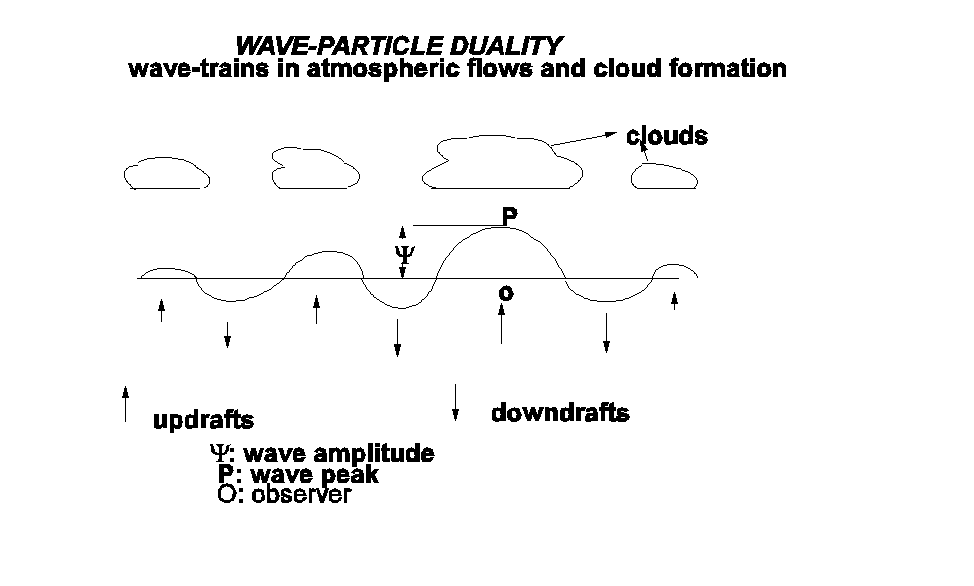
WAVE-PARTICLE DUALITY IN CLOUD FORMATION

The apparent paradox of wave-particle duality
in microscopic scale quantum systems is however physically
consistent in the context of macroscale atmospheric flows since
the bi-directional energy flow structure of a complete
atmospheric eddy results in the formation of clouds in updrafts
regions and dissipation of clouds in downdrafts regions.The
commonplace occurrence of clouds in a row is a manifestation of
wave-particle duality in the macroscale quantum system of
atmospheric flows. The above-described analogy of quantum-like
mechanics for atmospheric flows is similar to the concept of a
subquantum level of fluctuations whose space- time organization
gives rise to the observed manifestation of subatomic
phenomena,i.e.,quantum systems as order out of chaos
phenomena[G.Grossing,Il Nuovo Cimento 103B(1989) 497].
H.E.Puthoff[Phys.Rev.A.39,2333(1989)] has also put forth the
concept of "Gravity as a zero-point fluctuation
force"( Quantum
fluctuations of empty space).The vacuum zero-point
fluctuation(electromagnetic) energy manifested in the Casimir
effect is analogous to the turbulent scale fluctuations whose
spatial integration results in coherent large eddy structures.